With amendment 4 of the BS7617 being published in April 2026, various modifications to current regulations are to be announced regarding medical locations. Amendment 4 has been revised to help align the UK wiring regulations with the Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) that are utilised by the NHS and adopted by some FM companies working in the health sector. The requirement for Equipotential Bonding Busbars (EBB) inspection and testing has not changed and is not something that is new, amendment 4 of BS7671 has described the requirements in a clearer manner.
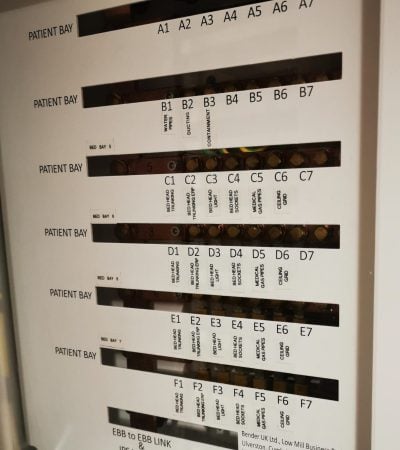
An Equipotential Bonding Busbar acts as a central connection point for supplementary protective equipotential bonding conductors within medical locations. These conductors connect exposed metalwork, services, and socket outlets to reduce touch voltages and minimise the risk of electric shock.
EBBs are a mandatory requirement in Group 1 and Group 2 medical locations, where applied medical equipment is in use and patient risk is higher.
Electrical safety in medical environments is critical. Patients are often more vulnerable to electric shock, and the consequences of electrical failure can be severe. Equipotential Bonding Busbars (EBBs) play a vital role in managing this risk by ensuring all exposed conductive parts and socket earths within patient areas are maintained at the same electrical potential.
Guardian Electrical provides specialist inspection and testing of EBB systems in medical locations, supporting duty holders in meeting the requirements of BS 7671 Section 710 and the latest Amendment 4 of the BS7671.
Historically, EBB testing has often been omitted from routine inspection regimes, particularly where specialist contractors maintain medical IT systems. This creates a significant compliance gap for duty holders.
Amendment 4 – What’s Changing?
Amendment 4 to BS 7671 (effective April 2026) strengthens and clarifies Section 710 requirements. Key updates include:
- Clearer wording aligned with HTM 06-01 and HTM 06-02
- Explicit requirement for end-to-end resistance testing of supplementary bonding conductors
- Introduction of Annex B710, a standardised template report for EBB inspection and testing
- Improved clarity around documentation, diagrams, and record-keeping
For the first time, Amendment 4 sets a clear benchmark for how EBB compliance should be evidenced.
Section 710 introduces additional inspection and testing requirements beyond a standard Electrical Installation Condition Report (EICR). These include:
Annual verification of supplementary protective equipotential bonding
Measurement of end-to-end resistance of bonding conductors
Verification of EBB connectivity and labelling
Accurate records, schedules, and diagrams of connected conductors
Medical Locations
Medical locations are classified into Group 0, Group 1, or Group 2, depending on the level of patient risk should an electrical fault or supply failure occur. This classification directly affects the earthing system, bonding requirements, and inspection and testing obligations. Correct classification is essential and should be agreed with clinical staff for new installations or assessed carefully in existing premises.
Medical location groups are defined in BS 7671 as:
Group 0 Medical Location – Medical location where no applied parts are intended to be used and where discontinuity (failure) of the supply cannot cause danger to life.
Group 1 Medical Location – A medical location where discontinuity of the supply does not represent a threat to the safety of the patient and applied parts are intended to be used:
- Externally
- Invasively to any part of the body except where Group 2 applies
Group 2 Medical Location – A medical location where and applied parts are intended to be used, and where discontinuity of the supply can cause danger to life, in applications such as:
- Intracardiac procedures
- Vital treatments and surgical operations
Once medical locations are determined on site, the appropriate testing program can be created. An example of group classifications can be seen in Annex A710 of Section 710.
They apply to a wide range of facilities, including:
-
Hospitals
-
Private Healthcare Facilities
-
Dental & Medical Facilities
-
Healthcare Centres
-
Medical Rooms within Workplaces
-
Medical Research Facilities involving Patients
Guardian Scope of Works
Based on the latest Amendment 4 requirements, Guardian Electrical have developed a complete program of works to ensure that all EBBs and associated requirements are tested as per the current British regulations and code of practice requirements.
Regulations within the BS7671 are not retrospective, meaning that even though several amendments have since modified the original Requirements for Electrical Installations book itself, an older installation can still satisfy the Electricity at Work Regulations 1989.
The Guardian scope of testing is divided into two categories, “1st Stage” and “2nd Stage”. Although regulations regarding the testing and maintenance of Equipotential Bonding Bars have always existed within the BS7671, the requirements have changed, and a focus has been heavily placed on Part 7 – Special Locations.
Regulations
In accordance with the BS7671:2018, specifically regulation 710.651 (ii) frequency of inspection & testing for Equipotential Bonding Bars should be completed annually, as stated –
“Annually – Measurements to verify that the resistance of the supplementary protective equipotential bonding is within limits stipulated by Regulation 710.415.2.2 and recorded in the same format required by Regulation 710.514.9.1 (vii).”
Following an annual inspection and testing, thorough record keeping is required, as per Regulation 710.514.9.1 (vii), which states –
“Plans of electrical installation together with records, drawings, wiring diagrams and modifications relating to the medical location, shall be provided.
(vii) record schedule and test data for the supplementary protective equipotential bonding system, including the connected item, size of conductor and resistance measurement.”
In accordance with the BS7671:2018, inspection & testing of EBBs are required be undertaken annually due to the classification of “Special Location – Medical Location” and therefore, can be added onto any existing or new electrical inspection & testing programme.
Download The Health Technical Memorandum (HTM) 06-01
Electrical services supply and distribution
Read The impact of Amendment 4:2026 on the 18th Edition of the IET Wiring Regulations
We're happy to help, contact us today...
To download our Medical case study, please click here.
